1. 概述
现在越来越多的AI训练选择用镜像的方式进行,然而tensorflow等镜像的大小要远大于一般镜像(dockerhub上tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-devel-gpu有3.19GB,同比centos:latest只有约234MB),如此庞大的镜像给AI训练带来较大的镜像拉取时延。然而,在AI训练场景下,镜像内的许多文件可能是不需要去访问的(例如tensorflow镜像内的自带数据集等),基于这一切入点,一种基于“懒”加载的镜像延迟加载技术被提出,极大的降低了镜像的拉取时延。
1.1 overlayFS和容器镜像加载
为了介绍镜像延迟加载的技术,了解overlayFS和docker的镜像加载过程是必要的。
overlayFS是一种堆叠文件系统,并于2014年合并入Linux内核,在docker1.12后推出的overlay2在inode的利用方面比overlay更有效,至于为何有效我会放到这一小节末尾介绍,这里我先简要介绍一下overlay2。overlay2的基本结构如下图所示。
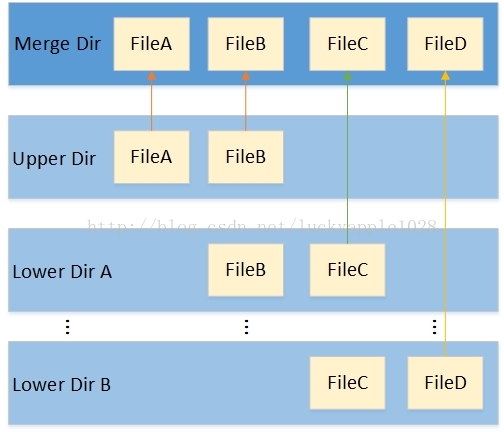
overlay2的读写场景如下,其中容器层Upper Dir,镜像层就是所有Lower Dir:
- 读的文件不在容器层:如果读的文件不在容器层,则从镜像层进行读
- 读的文件只存在在容器层:直接从容器层读
-
读的文件在容器层和镜像层:读容器层中的文件,因为容器层隐藏了镜像层同名的文件
- 写的文件不在容器层,在镜像层:由于文件不在容器层,因此
overlay/overlay2存储驱动使用copy_up操作从镜像层拷贝文件到容器层,然后将写入的内容写入到文件新的拷贝中。如果是新增文件,其上层目录会和底层layer进行merge操作合并为新的目录 - 删除文件和目录:删除镜像层的文件,会在容器层创建一个
whiteout文件来隐藏它;删除镜像层的目录,会创建opaque目录,它和whiteout文件有相同的效果 - 重命名目录:对一个目录调用
rename仅仅在资源和目的地路径都在顶层时才被允许,否则返回EXDEV
overlay是docker的存储驱动之一,docker里镜像驱动被抽象为graphdriver,每个镜像驱动(如overlay,aufs等)都实现了graphdriver的接口,通过fuse或内核态挂载对镜像的生命周期进行管理;而在containerd中,类似的模块叫做snapshotter,这个模块也是镜像延迟加载的关键,会在之后的章节详细介绍。
这里用ubuntu镜像来反应overlayFS的结构,执行docker pull ubuntu:latest后,镜像的拉取和解压会分层并行进行。docker在拉取镜像时会经过解析registry,解析镜像名,解析镜像tag,配置认证信息等步骤,在所有步骤执行完毕后docker的根目录内有如下的结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[root@VM_244_112_centos /var/lib/docker/overlay2]# tree -L 2
.
├── 91c6e5cc41f59fe3b914f368e7864ad4d708120069f7443c2c14e3ebb7adf688
│ ├── diff
│ └── link
├── b4c8df66bd6bb6a06630bde87364d41cebcc7a311d7f3958159420d27ddee6a5
│ ├── diff
│ ├── link
│ ├── lower
│ └── work
├── e45ca749ade1f4cf41cb81dd210a4761023bcefd8523039b22d8a5e768684a20
│ ├── diff
│ ├── link
│ ├── lower
│ └── work
└── l
├── 4SMJFTXKOSE3KIMJADFEHEIPOC -> ../b4c8df66bd6bb6a06630bde87364d41cebcc7a311d7f3958159420d27ddee6a5/diff
├── JMHFXUR2BPPIHDY53N7AWQFYHQ -> ../e45ca749ade1f4cf41cb81dd210a4761023bcefd8523039b22d8a5e768684a20/diff
└── SSNCTFQYZMQSONPRWRXBQW4W6P -> ../91c6e5cc41f59fe3b914f368e7864ad4d708120069f7443c2c14e3ebb7adf688/diff
12 directories, 5 files
ubuntu的镜像有3层layer,其中l目录中包含符号链接作为缩短的层标示符,这些标识符用来避免挂载时超过页面大小的限制,可以观察到每个link都是指向ubuntu其中一个镜像层的diff目录。同样,每个层目录的link文件也记录着该层的缩短标识符。
1
2
3
4
[root@VM_244_112_centos /var/lib/docker/overlay2/91c6e5cc41f59fe3b914f368e7864ad4d708120069f7443c2c14e3ebb7adf688]# cat link
SSNCTFQYZMQSONPRWRXBQW4W6P
[root@VM_244_112_centos /var/lib/docker/overlay2/91c6e5cc41f59fe3b914f368e7864ad4d708120069f7443c2c14e3ebb7adf688]# ll ../l | grep SSNCTFQYZMQSONPRWRXBQW4W6P
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 72 Dec 22 19:16 SSNCTFQYZMQSONPRWRXBQW4W6P -> ../91c6e5cc41f59fe3b914f368e7864ad4d708120069f7443c2c14e3ebb7adf688/diff
层目录中的lower文件记录了下层layer的缩短标识符(即l目录下的标识符),注意底层layer是没有lower文件的。
1
2
3
4
[root@VM_244_112_centos /var/lib/docker/overlay2/b4c8df66bd6bb6a06630bde87364d41cebcc7a311d7f3958159420d27ddee6a5]# ls
diff link lower work
[root@VM_244_112_centos /var/lib/docker/overlay2/b4c8df66bd6bb6a06630bde87364d41cebcc7a311d7f3958159420d27ddee6a5]# cat lower
l/SSNCTFQYZMQSONPRWRXBQW4W6P
每层目录下的work目录用来完成诸如copy-on-write的操作。
此时拉起一个ubuntu:latest的容器,cc85d9b18e2e79ff63045ef531aef9e224db23662652c3fbb923f765e5d185a0-init和cc85d9b18e2e79ff63045ef531aef9e224db23662652c3fbb923f765e5d185a0两个文件夹会出现在overlay2的目录下。查看这两个目录的内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
[root@VM_244_112_centos /var/lib/docker/overlay2/cc85d9b18e2e79ff63045ef531aef9e224db23662652c3fbb923f765e5d185a0]# tree -L 2 /var/lib/docker/overlay2/cc85d9b18e2e79ff63045ef531aef9e224db23662652c3fbb923f765e5d185a0*
/var/lib/docker/overlay2/cc85d9b18e2e79ff63045ef531aef9e224db23662652c3fbb923f765e5d185a0
├── diff
├── link
├── lower
├── merged
│ ├── bin -> usr/bin
│ ├── boot
│ ├── dev
│ ├── etc
│ ├── home
│ ├── lib -> usr/lib
│ ├── lib32 -> usr/lib32
│ ├── lib64 -> usr/lib64
│ ├── libx32 -> usr/libx32
│ ├── media
│ ├── mnt
│ ├── opt
│ ├── proc
│ ├── root
│ ├── run
│ ├── sbin -> usr/sbin
│ ├── srv
│ ├── sys
│ ├── tmp
│ ├── usr
│ └── var
└── work
└── work
/var/lib/docker/overlay2/cc85d9b18e2e79ff63045ef531aef9e224db23662652c3fbb923f765e5d185a0-init
├── diff
│ ├── dev
│ └── etc
├── link
├── lower
└── work
└── work
30 directories, 4 files
其中init为初始层,容器初始化时需要注入容器的信息都会放在初始层中(如主机信息,域名服务文件等),对容器作出改变的操作都在读写层完成。
1
2
3
4
# 容器内创建一个test文件
root@aa161ee6e328:/# echo test > test
root@aa161ee6e328:/# ls
bin boot dev etc home lib lib32 lib64 libx32 media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys test tmp usr var
1
2
3
4
5
# 该容器镜像层下的验证
[root@VM_244_112_centos /var/lib/docker/overlay2/cc85d9b18e2e79ff63045ef531aef9e224db23662652c3fbb923f765e5d185a0]# cat ./diff/test
test
[root@VM_244_112_centos /var/lib/docker/overlay2/cc85d9b18e2e79ff63045ef531aef9e224db23662652c3fbb923f765e5d185a0]# cat ./merged/test
test
overlay2支持多层lower层(最多支持128个),而overlay只支持两层(一个lower层,一个upper层),在overlay中,下层文件在上层中是以hard link的形式存在,而在linux操作系统中hard link会消耗inode,这也是为何overlay2对比overlay能节省更多inode的原因。
1.2 为什么
在整个容器拉起过程中,镜像加载占据了大部分时间。在Harter[3]的调查中,拉取镜像文件占据了76%的容器拉起时间,但是镜像内只有6.4%的内容被读取,在AI训练场景下这一问题更加突出。如概述所述,AI训练相关镜像动辄达到GB数量级,拉取会产生大量时延,但大部分耗时却花销在了不会访问的镜像内容上,降低了AI训练的效率。
1.3 传统方案
-
镜像缓存/预加载
传统方案就是在母机上缓存拉取过的镜像层(当然,docker已经支持了这一功能),并配置
pod的imagePolicy为IfNotPresent,镜像的分层让不同镜像之间可以对层进行共享,从而减少拉取其他镜像的时延。
同样的,预加载也是在母机上预先加载一部分关键镜像(例如
tensorflow,ubuntu等),拉取其他镜像时,部分镜像层会命中镜像仓库的缓存,从而降低拉取时延。但是这种方法在
cold start(例如刚刚上架的母机上没有缓存的镜像)或imagePolicy为Always的场景下表现不佳,且预加载只能缓解部分镜像的时延,为了增加命中,也会消耗大量母机的磁盘空间。 -
减小镜像大小
这种方法成本较高(需要人工修改镜像),且不适用于部分AI镜像。
2. 原理
镜像延迟加载的原理一句话概括便是只拉取镜像的索引文件,在用户挂载访问镜像时“懒惰”的拉取镜像内容。
2.1 术语
CRFS:一种基于FUSE的文件系统,支持直接从远程registry镜像仓库挂载镜像到本地stargz:CRFS依赖的镜像格式,由于传统的targz压缩无法索引且乱序,CRFS的挂载需要可索引、有序的stargz格式压缩文件estargz:stargz的一种优化,在stargz基础上利用prefetch landmark区分高低优先文件,高优文件会直接拉取snapshotter:管理镜像本地状态变化和挂载的containerd模块,每个snapshotter都有一个对应的文件系统remote layer:可支持远程挂载的镜像层,例如stargz格式的镜像内每一层都是remote layerremote snapshotter:支持挂载remote layer的snapshotter
2.2 CRFS和stargz
CRFS是一种FUSE文件系统,它允许用户直接从镜像仓库挂载镜像到本地而不需要通过拉取。它的挂载和overlay类似,事实上,stargz格式的镜像也可以直接用overlay`文件系统挂载。
CRFS的代码通过Golang的fuseAPI实现类似overlay2的文件系统,可以在这里查看,这里不再展开。
2.2.1 tar文件
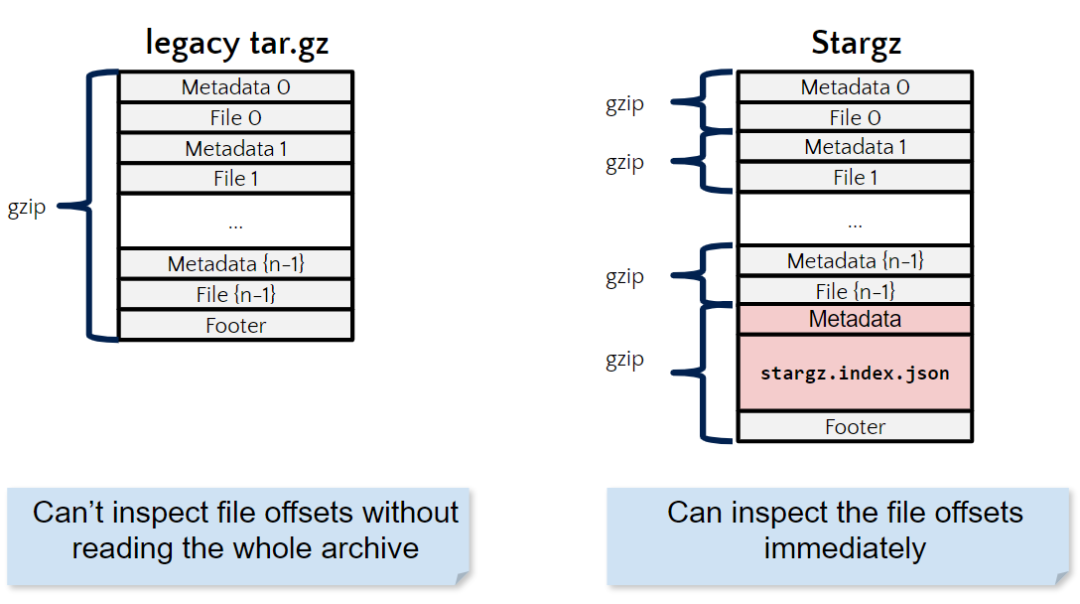
目前容器镜像都是由tar.gz文件表示,gzip流是不可搜索,且tar文件也没有索引,因此即使要读取1KB的文件也需要从远程镜像仓库拉取整个镜像,这种文件格式并不支持CRFS的挂载。
同时,符合OCI格式的镜像是以层为单位进行校验,而CRFS需要以文件为单位进行校验。
tar.gz的压缩格式为Gzip(TarF(file1) + TarF(file2) + TarF(file3) + TarFooter))
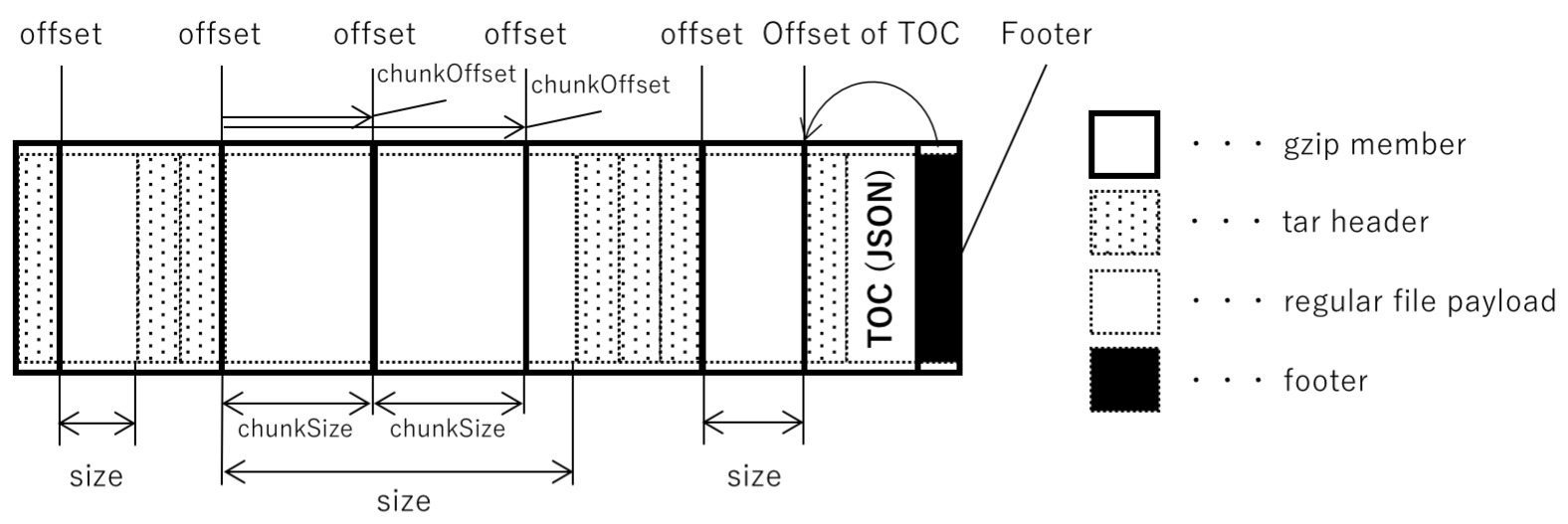
2.2.2 stargz文件
stargz的文件格式为Gzip(TarF(file1)) + Gzip(TarF(file2)) + Gzip(TarF(file3_chunk1)) + Gzip(F(file3_chunk2)) + Gzip(F(index of earlier files in magic file), TarFooter),tar.gz和stargz的对比如下图所示。
#### 2.2.3 estargz文件
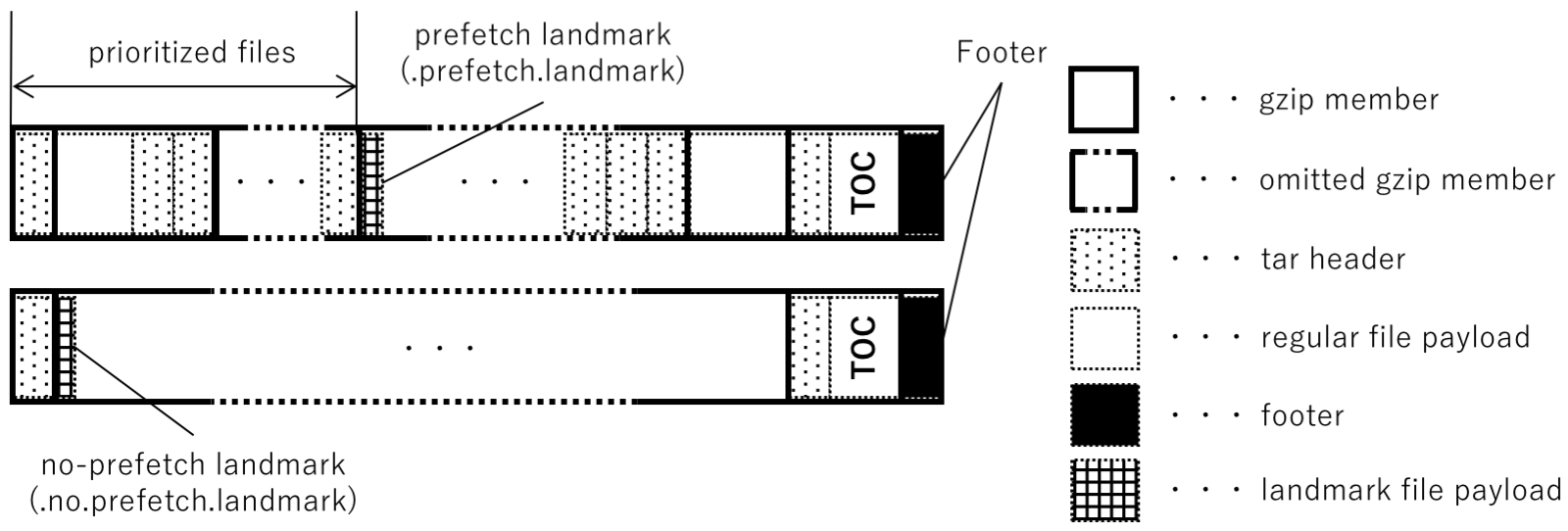
`estargz`文件通过`landmark`类型的文件区分需要优先拉取的文件内容,在`landmark`前的文件作为优先文件会在拉取镜像时直接被拉取,在预拉取和普通拉取之间找到一个平衡点。
### 2.3 containerd和snapshotter
#### 2.3.1 containerd
Containerd 是一个工业级标准的容器运行时,它强调简单性、健壮性和可移植性。Containerd 可以在宿主机中管理完整的容器生命周期:容器镜像的传输和存储、容器的执行和管理、存储和网络等。
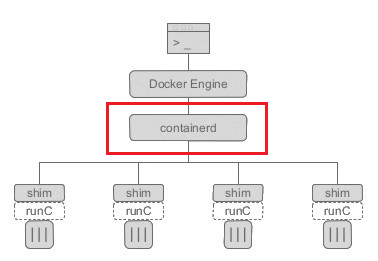
目前`docker`创建镜像的流程之一就是调用`containerd`的`grpc`接口,它通过调用`cri`创建容器,目前`k8s`支持直接对接`containerd`。它的架构如下图所示。
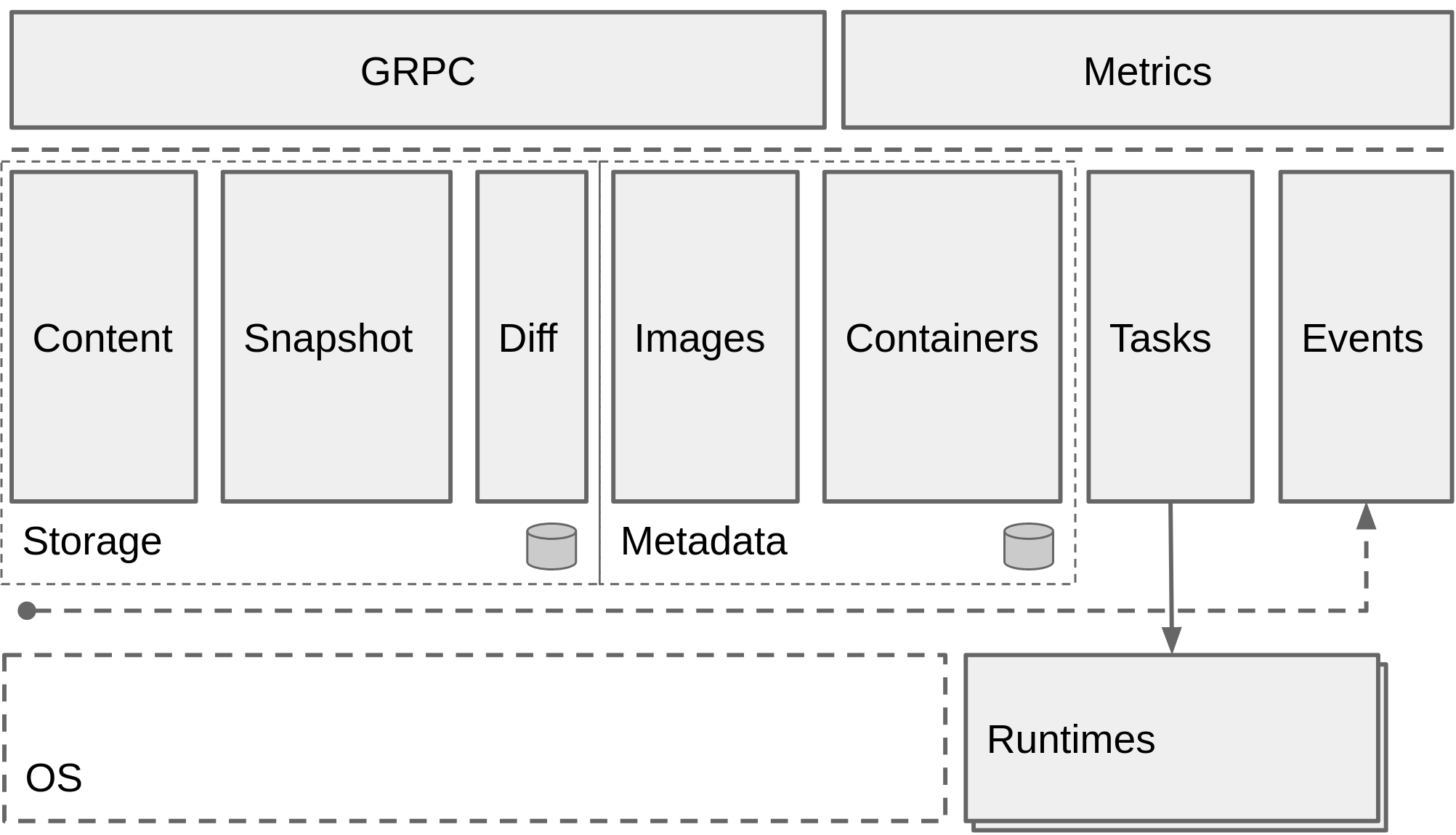
#### 2.3.2 snapshotter
其中`snapshotter`负责镜像的挂载和状态转换(类似`docker`的`graphdriver`),它允许符合`OCI`标准的镜像能在不通的操作系统上运行,不同于`graphdriver`,它是一种更加灵活的模型,除提供基本的挂载和快照的功能外,它和镜像结构的耦合没有那么紧密。它的API定义如下,可以在[containerd的源码](https://github.com/containerd/containerd/blob/master/snapshots/snapshotter.go)内查看API的详细定义。

**`snapshotter`提供了分配、快照和挂载抽象且基于层结构的文件系统的API,我们可以认为每种snapshotter都对应一种分层的文件系统**,一个`snapshot`的状态流转可用下图表示。
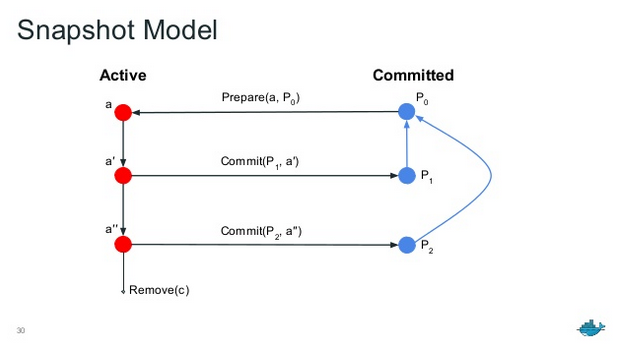
`snapshot`反映了一个文件系统的状态,每个`snapshot`都有一个父节点,父子节点间的差别可以转化为一个`layer`(类似于`docker`的`graphdriver`)。`Committed`状态的`snapshot`可以通过`Prepare`调用转化为`Active`,反之用`Commit`调用。`Active`状态的`snapshot`就是我们正在用的容器,容器内做的所有修改操作都可以通过`Commit`转化为一个新的`layer`,从而获得一个子镜像。
在`containerd`的源码中,每种分层文件系统都对应一种`snapshotter`(例如`overlay`,`zfs`等),在镜像延迟加载中,抽象化的`snapshotter`允许开发者针对`CRFS`文件系统提供一个插件,在镜像拉取时通过指定`snapshotter`实现拉取的具体操作,并把延迟加载拉取需要的信息通过`label`打入镜像,在挂载时通过`fuse`的远程挂载`stargz`格式的镜像到本地,**这类`snapshotter`也被成为`remote snapshotter`**(`remote snapshotter`也需要对`containerd`的源码进行更改,目前只有`1.4.2`后的版本支持`remote snapshotter`)。
### 2.4 stargz-snapshotter
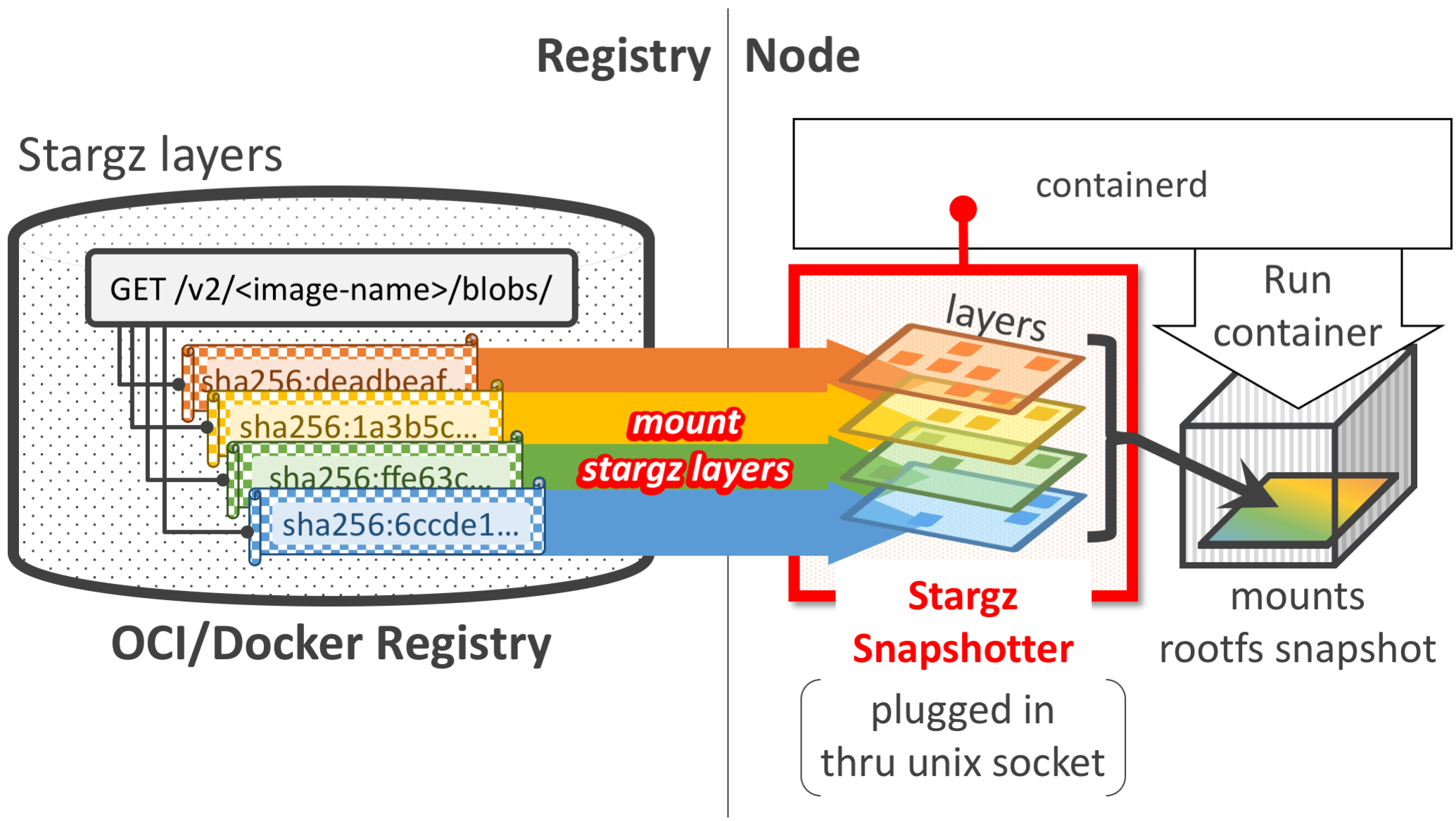
在了解`stargz`和`snapshotter`后,[`stargz-snapshotter`](https://github.com/containerd/stargz-snapshotter)便是两者的结合。
`stargz`格式的镜像层在拉取时会校验是否为`remote snapshotter`挂载的镜像,如果不是则拉取其内容,如果是则不拉取内容;随后镜像在运行时会转交给`stargz snapshotter`处理,对于一般的镜像直接解压缩,对`stargz`格式的镜像用镜像元数据进行远程挂载,最终拉起容器提供给用户。
由于镜像拉取和挂载在`containerd`中已经解耦,`remote snapshotter`在接手镜像前需要保证镜像内容没有被拉取,因此在拉取镜像时需要将使用的`snapshotter`传入并校验一个镜像层是否可以远程挂载,并将可以远程挂载的层过滤掉,具体改动在这个[commit](https://github.com/ktock/containerd/commit/53110e516e5b4c0cd5b81f61c01fd5e33a25edef#diff-1f8f50646891fcfbf8d89a7a4738f762R139)。
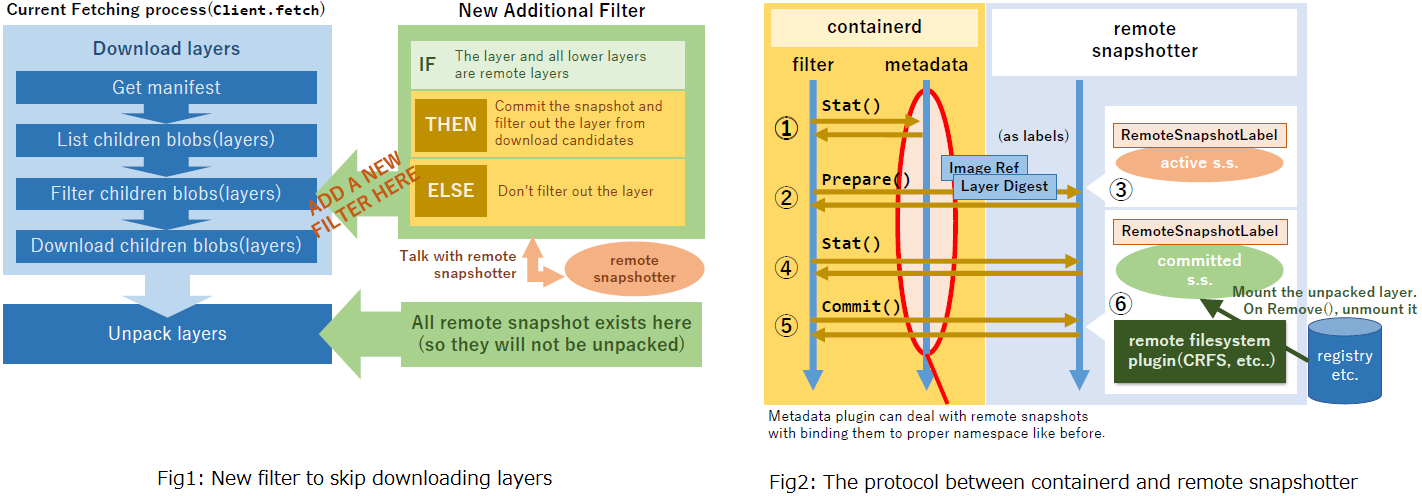
整体的流程如上图所示,一般镜像的拉起需要经过下载、解压、挂载的步骤,但是`remote snapshotter`并不需要下载、解压镜像的内容,在筛选`blob`的流程内如果检测到某个层是`remote layer`(通过镜像层的元数据检测),`remote snapshotter`会直接`commit`这个层,从而跳过下载和解压的过程。
## 3. 使用
`stargz-snapshotter`的作者已经预转化了多种镜像并做了实验,下面是他给出的数据。
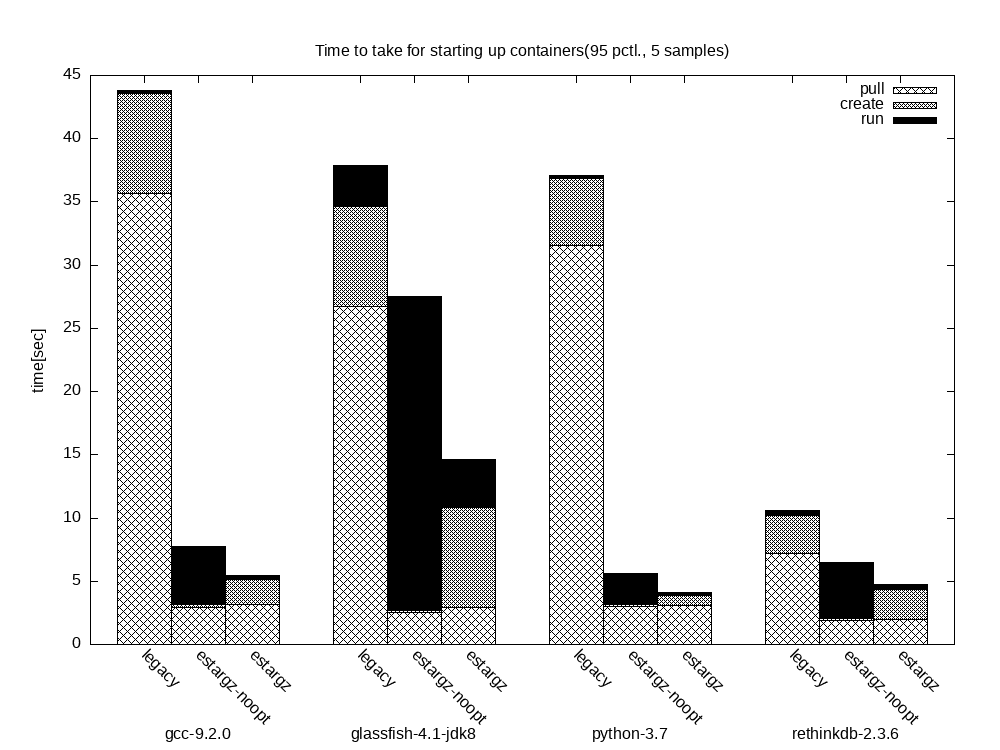
当然,在AI的场景下延迟加载的效果也需要重新验证,下面我来验证一下在`tensorflow`镜像上跑`benchmark`的效果。
### 3.1 环境配置
1. `kubelet`版本 >= 1.10(为了`CRI`对接`containerd`)
2. `containerd`版本 >= 1.4.2
3. `containerd`配置
```bash
# /etc/containerd/config.toml
# See also: https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kind/blob/fd64a56b0c3d5654eb6d22bce812e2a87eac5853/images/base/files/etc/containerd/config.toml
# explicitly use v2 config format
version = 2
# - Set default runtime handler to v2, which has a per-pod shim
# - Enable to use stargz snapshotter
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd]
default_runtime_name = "runc"
snapshotter = "stargz"
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc]
runtime_type = "io.containerd.runc.v2"
# Use stargz snapshotter
[proxy_plugins]
[proxy_plugins.stargz]
type = "snapshot"
address = "/run/containerd-stargz-grpc/containerd-stargz-grpc.sock"
# Use tencent registry
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri"]
sandbox_image = "csighub.tencentyun.com/k8s.gcr/pause:3.1" # 配置pause镜像源
- 通过作者给出的转化工具(教程)将
dockerhub上最新的tensorflow镜像转化为esgz格式,推送到registry上
3.2 stargz-snapshotter部署
kubelet对接containerd
1
2
# /etc/sysconfig/kubelet
KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=--container-runtime=remote --runtime-request-timeout=15m --container-runtime-endpoint=unix:///run/containerd/containerd.sock
- 部署
stargz-snapshotter
拉下repo直接make,编译出来的二进制通过如下service文件在systemctl上部署。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[Unit]
Description=containerd stargz snapshotter
Documentation=https://github.com/containerd/stargz-snapshotter
After=network.target
Before=containerd.service
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/containerd-stargz-grpc --address=/run/containerd-stargz-grpc/containerd-stargz-grpc.sock --config=/etc/containerd-stargz-grpc/config.toml
Restart=always
RestartSec=1
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
3.3 验证
- 普通镜像
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 3m30s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/tensorflow to k8s-cpu-node-1
Normal Pulling 3m27s kubelet, k8s-cpu-node-1 Pulling image "csighub.tencentyun.com/elihe/tensorflow:v1.0.5"
Normal Pulled 2s kubelet, k8s-cpu-node-1 Successfully pulled image "csighub.tencentyun.com/elihe/tensorflow:v1.0.5"
Normal Created 2s kubelet, k8s-cpu-node-1 Created container tensorflow
Normal Started 2s kubelet, k8s-cpu-node-1 Started container tensorflow
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:493: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_qint8 = np.dtype([("qint8", np.int8, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:494: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_quint8 = np.dtype([("quint8", np.uint8, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:495: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_qint16 = np.dtype([("qint16", np.int16, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:496: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_quint16 = np.dtype([("quint16", np.uint16, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:497: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_qint32 = np.dtype([("qint32", np.int32, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:502: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
np_resource = np.dtype([("resource", np.ubyte, 1)])
WARNING:tensorflow:From /benchmarks/scripts/tf_cnn_benchmarks/benchmark_cnn.py:1120: Supervisor.__init__ (from tensorflow.python.training.supervisor) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Please switch to tf.train.MonitoredTrainingSession
TensorFlow: 1.5
Model: trivial
Dataset: imagenet (synthetic)
Mode: training
SingleSess: False
Batch size: 64 global
64.0 per device
Devices: ['/cpu:0']
Data format: NHWC
Layout optimizer: False
Optimizer: sgd
Variables: parameter_server
==========
Generating model
Running warm up
Done warm up
Step Img/sec loss
1 images/sec: 513.7 +/- 0.0 (jitter = 0.0) 7.055
10 images/sec: 518.4 +/- 4.5 (jitter = 15.4) 7.055
20 images/sec: 517.8 +/- 3.2 (jitter = 17.8) 7.055
30 images/sec: 521.5 +/- 2.4 (jitter = 11.6) 7.055
40 images/sec: 520.1 +/- 2.3 (jitter = 13.1) 7.055
50 images/sec: 519.2 +/- 2.2 (jitter = 12.8) 7.055
60 images/sec: 518.0 +/- 2.0 (jitter = 14.5) 7.055
70 images/sec: 517.2 +/- 1.8 (jitter = 14.8) 7.055
80 images/sec: 515.3 +/- 1.9 (jitter = 15.6) 7.055
90 images/sec: 513.7 +/- 1.9 (jitter = 17.0) 7.055
100 images/sec: 514.2 +/- 1.7 (jitter = 16.7) 7.055
110 images/sec: 513.3 +/- 1.6 (jitter = 17.7) 7.055
120 images/sec: 512.6 +/- 1.6 (jitter = 18.6) 7.055
130 images/sec: 513.1 +/- 1.5 (jitter = 17.5) 7.055
140 images/sec: 512.7 +/- 1.4 (jitter = 19.1) 7.055
150 images/sec: 512.6 +/- 1.4 (jitter = 20.2) 7.055
160 images/sec: 512.6 +/- 1.4 (jitter = 19.9) 7.055
170 images/sec: 513.1 +/- 1.3 (jitter = 19.3) 7.055
180 images/sec: 512.9 +/- 1.3 (jitter = 20.0) 7.055
190 images/sec: 512.9 +/- 1.3 (jitter = 20.0) 7.055
200 images/sec: 513.5 +/- 1.2 (jitter = 19.8) 7.055
210 images/sec: 513.8 +/- 1.2 (jitter = 19.0) 7.055
220 images/sec: 514.0 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 18.6) 7.055
230 images/sec: 513.9 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 18.7) 7.055
240 images/sec: 514.5 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 18.4) 7.055
250 images/sec: 514.4 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 18.6) 7.055
260 images/sec: 514.8 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 18.6) 7.055
270 images/sec: 514.6 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 18.7) 7.055
280 images/sec: 514.8 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.6) 7.055
290 images/sec: 515.1 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.6) 7.055
300 images/sec: 515.2 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.2) 7.055
310 images/sec: 515.2 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.2) 7.055
320 images/sec: 515.2 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 17.7) 7.055
330 images/sec: 515.3 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.5) 7.055
340 images/sec: 515.4 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.9) 7.055
350 images/sec: 515.6 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.5) 7.055
360 images/sec: 515.5 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.5) 7.055
370 images/sec: 515.6 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.5) 7.055
380 images/sec: 515.8 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.4) 7.055
390 images/sec: 515.3 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.8) 7.055
400 images/sec: 515.1 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 18.4) 7.055
410 images/sec: 514.6 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 18.7) 7.055
420 images/sec: 514.1 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 19.4) 7.055
430 images/sec: 512.5 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 20.2) 7.055
440 images/sec: 512.3 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 20.3) 7.055
450 images/sec: 512.3 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 20.5) 7.055
460 images/sec: 511.9 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 20.7) 7.055
470 images/sec: 511.5 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 21.0) 7.055
480 images/sec: 511.1 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 21.3) 7.055
490 images/sec: 510.8 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 21.3) 7.055
500 images/sec: 510.7 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 21.1) 7.055
----------------------------------------------------------------
total images/sec: 511.38
----------------------------------------------------------------
esgz镜像
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 6s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/tensorflow-esgz to k8s-cpu-node-1
Normal Pulling 5s kubelet, k8s-cpu-node-1 Pulling image "csighub.tencentyun.com/elihe/tensorflow:v1.0.5-esgz"
Normal Pulled 0s kubelet, k8s-cpu-node-1 Successfully pulled image "csighub.tencentyun.com/elihe/tensorflow:v1.0.5-esgz"
Normal Created 0s kubelet, k8s-cpu-node-1 Created container tensorflow
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:493: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_qint8 = np.dtype([("qint8", np.int8, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:494: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_quint8 = np.dtype([("quint8", np.uint8, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:495: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_qint16 = np.dtype([("qint16", np.int16, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:496: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_quint16 = np.dtype([("quint16", np.uint16, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:497: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
_np_qint32 = np.dtype([("qint32", np.int32, 1)])
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/dtypes.py:502: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.
np_resource = np.dtype([("resource", np.ubyte, 1)])
WARNING:tensorflow:From /benchmarks/scripts/tf_cnn_benchmarks/benchmark_cnn.py:1120: Supervisor.__init__ (from tensorflow.python.training.supervisor) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Please switch to tf.train.MonitoredTrainingSession
TensorFlow: 1.5
Model: trivial
Dataset: imagenet (synthetic)
Mode: training
SingleSess: False
Batch size: 64 global
64.0 per device
Devices: ['/cpu:0']
Data format: NHWC
Layout optimizer: False
Optimizer: sgd
Variables: parameter_server
==========
Generating model
Running warm up
Done warm up
Step Img/sec loss
1 images/sec: 487.6 +/- 0.0 (jitter = 0.0) 7.055
10 images/sec: 505.9 +/- 3.5 (jitter = 14.3) 7.055
20 images/sec: 505.6 +/- 2.6 (jitter = 12.2) 7.055
30 images/sec: 505.5 +/- 2.4 (jitter = 15.7) 7.055
40 images/sec: 501.1 +/- 2.5 (jitter = 17.7) 7.055
50 images/sec: 500.8 +/- 2.1 (jitter = 18.3) 7.055
60 images/sec: 500.2 +/- 1.9 (jitter = 17.6) 7.055
70 images/sec: 500.5 +/- 1.8 (jitter = 16.1) 7.055
80 images/sec: 502.6 +/- 1.8 (jitter = 17.1) 7.055
90 images/sec: 504.3 +/- 1.7 (jitter = 16.5) 7.055
100 images/sec: 505.6 +/- 1.6 (jitter = 16.7) 7.055
110 images/sec: 507.6 +/- 1.6 (jitter = 18.4) 7.055
120 images/sec: 509.1 +/- 1.6 (jitter = 18.5) 7.055
130 images/sec: 509.0 +/- 1.6 (jitter = 18.4) 7.055
140 images/sec: 508.1 +/- 1.5 (jitter = 19.7) 7.055
150 images/sec: 508.9 +/- 1.5 (jitter = 17.5) 7.055
160 images/sec: 510.0 +/- 1.4 (jitter = 18.7) 7.055
170 images/sec: 510.5 +/- 1.4 (jitter = 19.9) 7.055
180 images/sec: 511.4 +/- 1.4 (jitter = 20.2) 7.055
190 images/sec: 511.6 +/- 1.3 (jitter = 20.7) 7.055
200 images/sec: 511.6 +/- 1.3 (jitter = 20.6) 7.055
210 images/sec: 511.8 +/- 1.3 (jitter = 20.7) 7.055
220 images/sec: 512.7 +/- 1.2 (jitter = 20.2) 7.055
230 images/sec: 512.8 +/- 1.2 (jitter = 19.9) 7.055
240 images/sec: 513.4 +/- 1.2 (jitter = 19.4) 7.055
250 images/sec: 513.7 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 18.8) 7.055
260 images/sec: 513.6 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 19.0) 7.055
270 images/sec: 514.0 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 19.0) 7.055
280 images/sec: 514.1 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 18.6) 7.055
290 images/sec: 514.4 +/- 1.1 (jitter = 18.7) 7.055
300 images/sec: 514.5 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.4) 7.055
310 images/sec: 514.7 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.2) 7.055
320 images/sec: 514.7 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.4) 7.055
330 images/sec: 514.8 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.8) 7.055
340 images/sec: 515.2 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.5) 7.055
350 images/sec: 515.1 +/- 1.0 (jitter = 18.8) 7.055
360 images/sec: 515.6 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 18.7) 7.055
370 images/sec: 515.9 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 18.5) 7.055
380 images/sec: 516.0 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 18.1) 7.055
390 images/sec: 516.2 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.7) 7.055
400 images/sec: 516.1 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.7) 7.055
410 images/sec: 516.3 +/- 0.9 (jitter = 17.7) 7.055
420 images/sec: 516.3 +/- 0.8 (jitter = 17.8) 7.055
430 images/sec: 516.7 +/- 0.8 (jitter = 17.5) 7.055
440 images/sec: 516.6 +/- 0.8 (jitter = 17.6) 7.055
450 images/sec: 516.8 +/- 0.8 (jitter = 17.6) 7.055
460 images/sec: 517.1 +/- 0.8 (jitter = 17.3) 7.055
470 images/sec: 517.0 +/- 0.8 (jitter = 17.6) 7.055
480 images/sec: 517.0 +/- 0.8 (jitter = 17.6) 7.055
490 images/sec: 517.0 +/- 0.8 (jitter = 17.8) 7.055
500 images/sec: 517.1 +/- 0.8 (jitter = 17.9) 7.055
----------------------------------------------------------------
total images/sec: 516.24
----------------------------------------------------------------
可以观察到esgz格式的镜像在行为一致的情况下拉取镜像的时间比普通快了将近3分钟。
本人也对小镜像做过实验,esgz镜像的拉取速度也在5秒左右,因为拉取行为实则是拉取元数据,因此对于转化后的镜像拉取时延几乎一致。
4. 小结
镜像延迟加载通过远程挂载特殊格式的镜像文件实现了镜像的“懒惰”拉取。对于小镜像来说,它的拉取时延优化并不明显(如之前所述,拉取耗时基本都在5秒左右),但是对于大镜像而言(尤其是AI训练的场景下),这种“懒惰”策略能优化大量的创建耗时。
当然,它也有其缺点,因为延迟加载的前提是“大部分镜像中的文件没有被用户访问”,在特殊场景下延迟加载的镜像会给用户的操作带来大量延迟(因为拉取镜像的时延被平均到了访问文件的网络IO中),目前只能通过estargz格式的文件将镜像内容切分为高低优来实现,但是这并不是一个长久之计。此外,延迟加载对网络的稳定性也有很大的要求(尤其是registry),在网络不稳定时容器的运行也会频繁被网络IO阻塞。
在这里延伸引入一下阿里的解决方案。
阿里将镜像拆分为元数据和数据两层(这种镜像格式被称为Rafs),其中元数据层是一颗自校验的哈希树,数据层切分为固定大小切片,数据可以被不同镜像的不同文件共享,如下图所示。
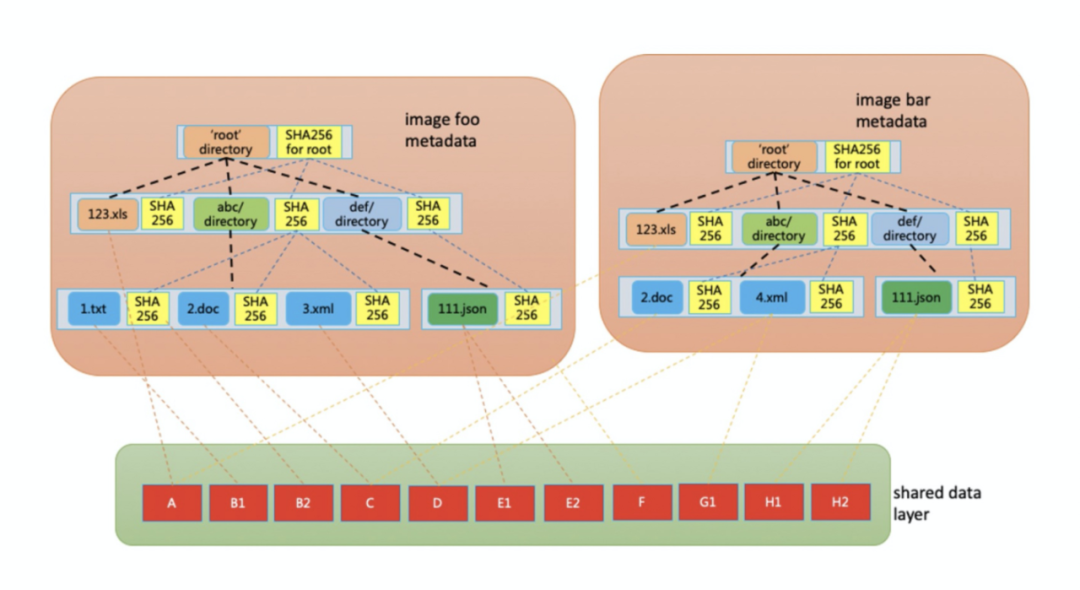
和stargz-snapshotter类似,Rafs也需要一个负责解析镜像格式的FUSE进程,这一套镜像的服务被称为Nydus。此外,阿里通过引入高可用P2P镜像文件分发系统Dragonfly来解决网络的问题。
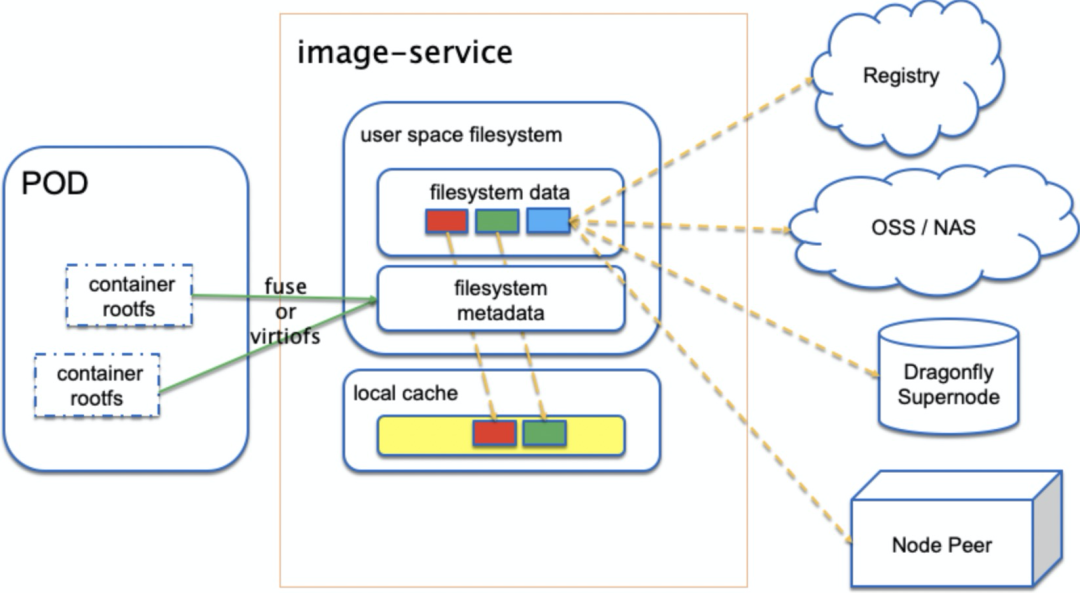
基于这个设计架构,Nydus在镜像的生命流程中做了如下的优化。
build环节:块级别镜像去重ship环节:支持不同镜像存储后端,和Dragonfly的p2p良好集成run环节:兼容OCI标准
5. reference
[1] https://arkingc.github.io/2017/05/05/2017-05-05-docke-filesystem-overlay/
[2] https://docs.docker.com/storage/storagedriver/overlayfs-driver/#how-the-overlay2-driver-works
[3] https://www.usenix.org/conference/fast16/technical-sessions/presentation/harter
[4] https://medium.com/nttlabs/startup-containers-in-lightning-speed-with-lazy-image-distribution-on-containerd-243d94522361
[5] https://www.cnblogs.com/sparkdev/p/9063042.html
[6] https://github.com/containerd/stargz-snapshotter/blob/master/docs/stargz-estargz.md
[7] https://github.com/containerd/containerd/issues/2943
[8] https://github.com/dragonflyoss/